Category: Artificial Intelligence
-
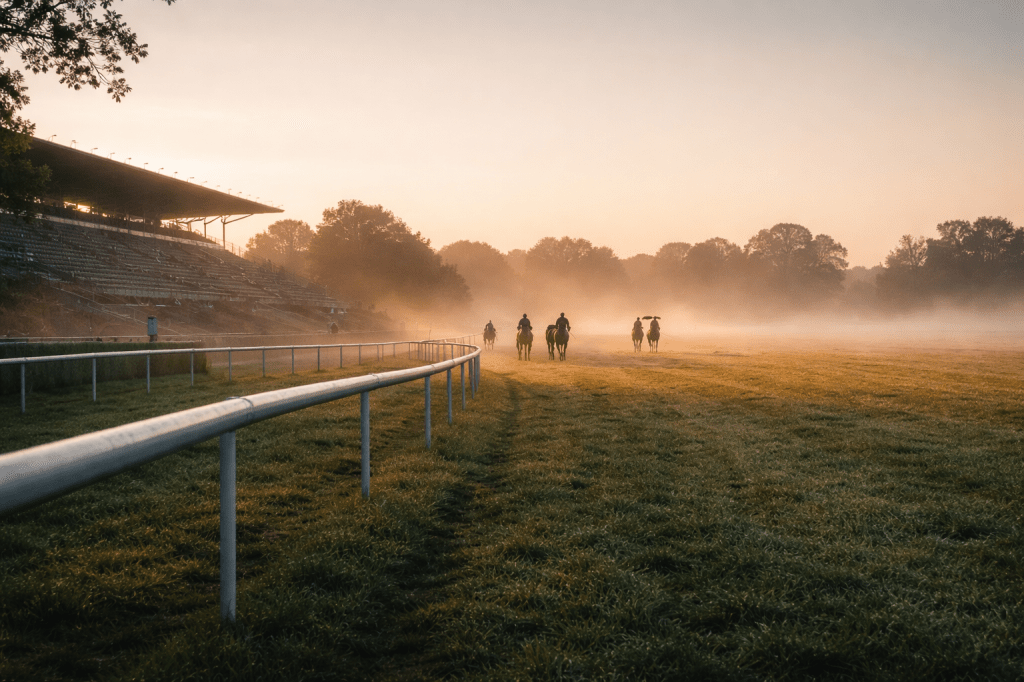
Predictive AI can mesmerise with dazzling historical wins, yet falters when faced with new data. Horse-racing experiments reveal that models succeed briefly, then unpredictably fail. In reactive systems, observation and expectation subtly alter outcomes. The lesson: respect the models, plan for chaos, and never mistake algorithms for control over the world.
-
We are unknowingly replaying an ancient script. By viewing the rise of AI through the lens of Sumerian myth and the Garden of Eden, we realise we have become the Gods we once feared. This is not a story of innovation, but a warning of cyclical obsolescence and the eternal return.
-
Humanity’s Top 10 Unanswered Questions
8–12 minutes·
·
Humanity’s most profound inquiries tackle the core of our existence, the nature of the universe, and our technological future. At the forefront is the search for life’s meaning, a question addressed by philosophy, religion, and science. Another major enigma is the nature of consciousness—our subjective awareness—which remains a “hard problem” for neuroscience. We persist in…
-
Lost languages and scripts hold silent histories. Decipherment, a human endeavour to reconnect with ancestors, involves detective-like analysis using clues like bilingual texts. Breakthroughs with Egyptian hieroglyphs, Linear B, and Mayan glyphs reveal past civilisations, with computational tools now aiding this quest to make ancient voices speak again.
-
Science provides powerful tools for understanding how things work, but philosophy tackles deeper questions about what we are, the nature of reality, and knowledge itself. It critically examines assumptions, complements scientific inquiry, and helps us understand the implications of our discoveries, proving essential in our quest for understanding.
-
Large Language Models (LLMs) are rapidly evolving, impacting work, creativity, and societal systems. While offering automation and educational benefits, they pose risks like misinformation, ethical biases, and intellectual property issues. Addressing these challenges through careful governance and adapting societal structures is crucial for managing their transformative power and future.
-
Classical computing reached limits where quantum effects interfere. Quantum computing emerged to harness these effects using qubits (superposition, entanglement) for problems classical computers can’t efficiently solve. Theory and algorithms paved the way, though building quantum machines is challenging, requiring classical control. They offer potential for simulations and cryptography, working alongside classical systems.
-
Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) has evolved from 1940s punch-card systems to intuitive voice assistants and gesture controls. Milestones include Douglas Engelbart’s 1968 interface innovations, 1980s graphical interfaces, and modern touchscreens. HCI prioritises user-centred design, blending human intuition with machine functionality. Advances like AI and brain-computer interfaces raise ethical questions, urging balance between technological empowerment and human…
-
From Steam to AI: Navigating Job Shifts and Future Opportunities
5–7 minutes·
·
Technology’s impact on employment, from the Industrial Revolution to today’s AI-driven shifts, involves both job displacement and creation. Automation threatens roles but spurs new industries like renewable energy and digital careers. Ethical concerns, such as biased algorithms, highlight the need for responsible innovation. Adaptability, tech literacy, and human-centric skills are crucial for future careers, balancing…
-
In the digital age, pervasive tracking fuels government surveillance concerns, blending security and intrusion. Historical programmes like COINTELPRO and Snowden’s NSA leaks reveal mass monitoring, while facial recognition and tech partnerships amplify distrust. Conspiracy theories, driven by secrecy and pop culture, merge documented realities with myths. Experts debate privacy erosion versus safety, questioning transparency’s role…
-
Biophysics combines biology and physics to decode life’s molecular mechanisms, from protein folding to cellular processes. Emerging in the mid-20th century, it builds on historical breakthroughs like DNA’s structure and Hodgkin-Huxley’s nerve models. Applications include MRI, drug design, and synthetic biology, while controversies surround CRISPR and AI-driven research. Future challenges involve quantum biology and ethical…
-
Natural Language Processing (NLP) evolved from 1950s rule-based systems like ELIZA to modern neural networks and transformers (e.g., GPT-3), enabling real-time translation, sentiment analysis, and virtual assistants. While revolutionising communication, education, and healthcare, NLP faces ethical challenges like bias and misinformation. Future advancements may integrate multimodal models and quantum computing, questioning machines’ true linguistic understanding.
-
Philosophy explores human nature through history, from Socrates’ rational inquiry to Sartre’s existentialism. Debates span essentialism (Plato, Aristotle) versus existential freedom, reason versus experience (Descartes, Locke), and societal roles (Stoics, Hobbes). Modern issues like AI, genetics, and ethics highlight philosophy’s ongoing relevance in understanding identity, morality, and humanity’s evolving challenges.
-
Cybersecurity’s evolution mirrors computing’s history, from WWII codebreaking to modern digital threats. Key milestones include the 1988 Morris Worm and 2007 Estonian attacks, highlighting vulnerabilities in interconnected systems. Core principles (confidentiality, integrity, availability) underpin defences like encryption and AI. Human error remains a weak link. Emerging challenges—quantum computing, IoT expansion—demand vigilance, blending technology with ethical…
-
Quantum AI Revolution
4–6 minutes·
·
Quantum AI is a rapidly evolving field that could revolutionise the way we live and work, with significant implications for various fields, but also raising important questions about ethics and safety.