Category: Engineering
-
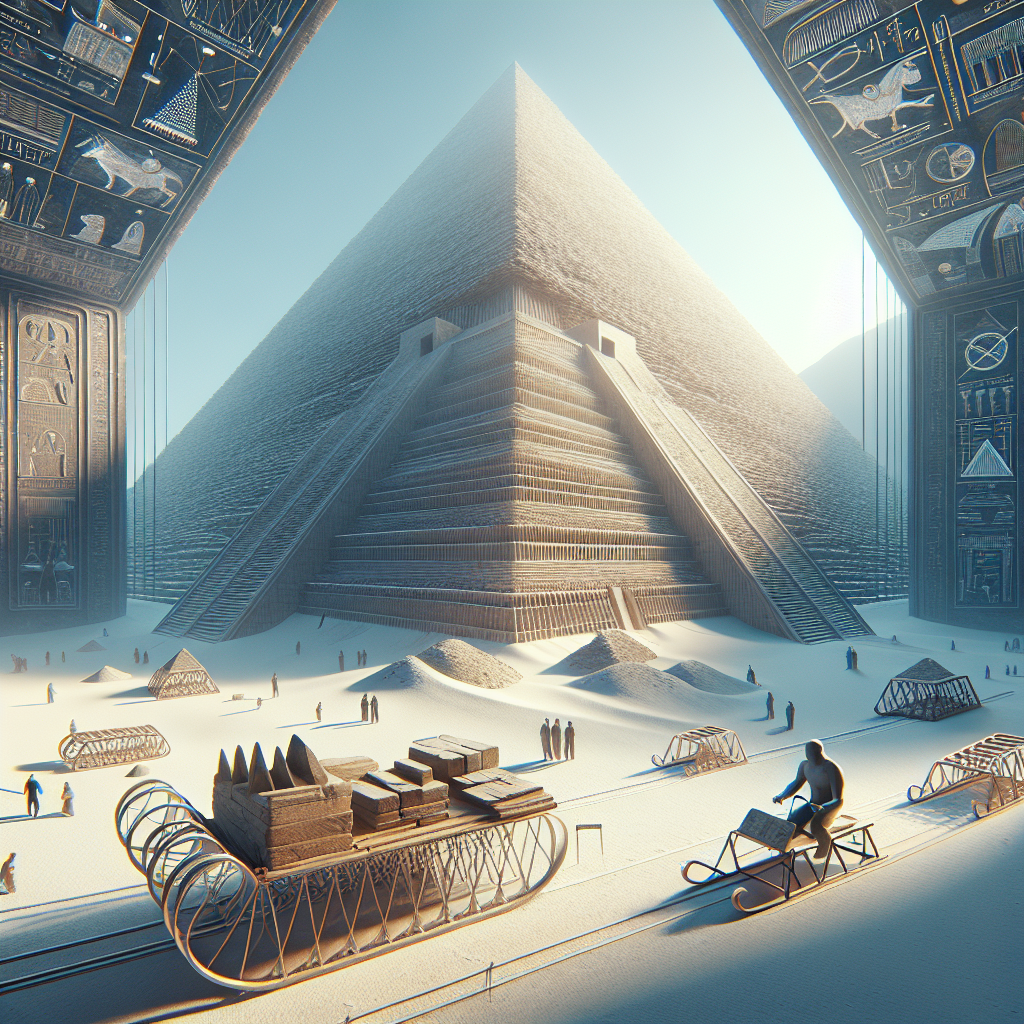
Ancient Egyptian architecture is a testament to the civilisation’s ingenuity, with iconic structures like the Pyramids of Giza and the Temple Complex at Karnak showcasing their grandeur and beauty, inspiring wonder and awe in people today, with a unique blend of technology and culture.
-
The Osireion and South American megalithic sites share similarities in massive stone blockwork, precision fitting, and engineering skills, despite differences in materials, sizes, and designs, showcasing ancient civilizations’ ingenuity and stoneworking abilities, with unique cultural and historical contexts.
-
The article explores the construction of pyramids, particularly in Egypt, discussing historical and modern theories, including internal ramps and sledges for transporting stone. It notes the socio-cultural significance of pyramids beyond tombs and highlights the challenge historians face in fully understanding their construction, which remains a captivating enigma.
-
The Industrial Revolution marked significant socio-economic transformation from the late 1700s to the early 19th century, originating in Britain. It brought technological breakthroughs, urbanization, and the rise of factories, impacting labor, global trade, attitudes toward wealth, and social classes, with effects still relevant today in the digital age.
-
Unlocking the Final Frontier: Humanity’s Path to the Stars
2–4 minutes·
·
Space colonisation fascinates humanity, driven by resource acquisition, environmental preservation, and survival. Asteroids and planets offer valuable resources, while space colonies could reduce Earth’s ecological strain. Ensuring human survival against catastrophic events like asteroid impacts is crucial. However, technical and ethical challenges persist, necessitating innovation, ethics, and international cooperation as humanity becomes a spacefaring civilization.
-
The conversation highlights the significance of sustainable architecture in combating climate change by prioritizing energy efficiency, sustainable materials, and reduced carbon footprints. It covers smart building technology, utilization of eco-friendly materials, and innovations like green roofs, emphasizing their environmental benefits. Regenerative design aims for a positive environmental impact, transforming future building interactions.